
Continuous Liquid – Liquid Extraction System.In case of change in densities K may not be constant. Since, C A I = ρ I*y A and C A II = ρ II*x A, Therefore, we can write phase equilibrium constant in terms of mass fraction as below Where, M is distribution coefficient, C A Iand C A II are the solute concentration (g/liter) at equilibrium state in Phase- I and Phase- II respectively.
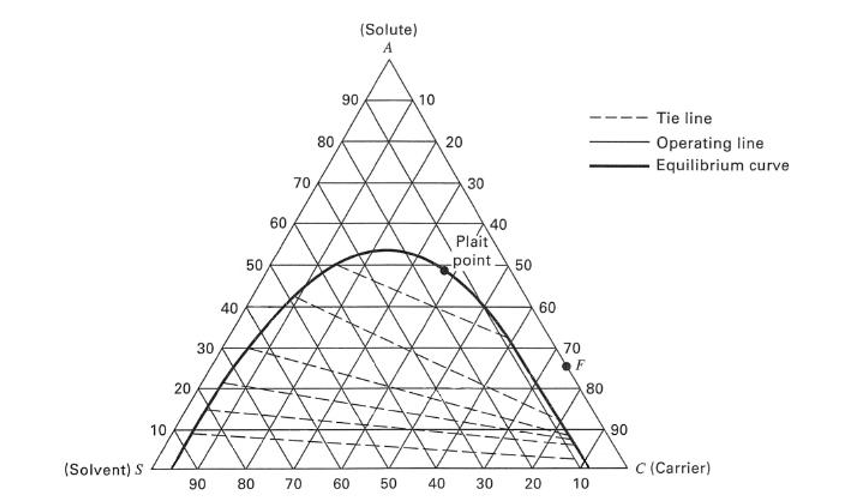
The ratio of solute concentration at equilibrium state between liquid Phase- I and liquid Phase- II is known as distribution coefficient and given by below expression. In which upper layer is light phase and bottom layer being heavy phase. After mixing when this mixture settles, two layers forms. In extraction process feed and solvent streams mixing enhance the solute transfer from feed to solvent stream. Selection of solvent for extraction is based on many criteria such as boiling point, environment friendly, cost and toxicity. And, other is solvent stream in which solute transfer takes place. However, the solvent which contain solute we consider it a feed stream. Moreover, both the solvents are insoluble in one another. In liquid-liquid extraction process solute is transferred between solvents. In plants liquid-liquid extraction column is used to separate components using solvent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
